

Funnels and Journey Maps
Jan 29, 2026
Marketing Funnels and User Journey Mapping: The Foundation of Strategic Business Growth
Understanding Marketing Funnels
What is a Marketing Funnel?
A marketing funnel is a visual representation of the customer journey from initial awareness of your brand to the final conversion action—and beyond. The funnel metaphor reflects a fundamental reality: not everyone who becomes aware of your business will become a customer. As prospects move through each stage, some drop off, resulting in a narrowing "funnel" shape.
1. Awareness Stage (Top of Funnel - TOFU)
At this initial stage, potential customers first become aware that your business, product, or service exists. They may not yet recognize they have a problem you can solve, or they're just beginning to identify their needs.
Marketing activities at this stage include:
Social media content and advertising
Blog posts and SEO-optimized content
Podcast appearances and PR efforts
Display advertising and brand awareness campaigns
2. Interest/Consideration Stage (Middle of Funnel - MOFU)
Prospects in this stage are actively researching solutions to their identified problem. They're comparing options, reading reviews, and consuming educational content to make informed decisions.
Marketing activities at this stage include:
Email nurture campaigns
Webinars and educational content
Case studies and white papers
Product comparison guides
3. Decision Stage (Bottom of Funnel - BOFU)
At this critical juncture, prospects are ready to make a purchase decision. They're evaluating final options and looking for that last piece of information or incentive to convert.
Marketing activities at this stage include:
Free trials or demos
Personalized consultations
Limited-time offers or discounts
Detailed product specifications and pricing information
4. Post-Conversion Stages
Modern marketing funnels don't end at conversion. Smart businesses recognize that retention, loyalty, and advocacy are equally important:
Retention: Keeping customers engaged and satisfied
Loyalty: Turning satisfied customers into repeat buyers
Advocacy: Transforming loyal customers into brand ambassadors
Identifying Target Audiences at Each Stage
Not all customers are created equal, and not all funnel stages require the same approach. Understanding who your audience is at each stage allows you to deliver precisely targeted messages that resonate.
Awareness Stage Audience:
Pain points: May not fully understand their problem
Information needs: Educational content, industry insights
Decision readiness: Very low
Best approach: Broad, engaging content that builds trust and authority
Consideration Stage Audience:
Pain points: Actively seeking solutions, overwhelmed by options
Information needs: Comparative content, detailed explanations
Decision readiness: Medium
Best approach: Targeted content that positions your solution favorably
Decision Stage Audience:
Pain points: Need reassurance, specific questions about implementation
Information needs: Proof of value, clear differentiation
Decision readiness: High
Best approach: Direct, conversion-focused messaging with clear calls-to-action
The Role of Data Analytics in Optimizing the Funnel
Data analytics transforms your marketing funnel from a theoretical framework into a powerful optimization engine. By tracking metrics at each stage, you can identify bottlenecks, understand drop-off points, and make data-driven improvements.
Key Metrics by Funnel Stage:

Analytics allows you to answer critical questions such as:
Which traffic sources bring the highest quality leads?
At which stage do most prospects drop off?
What content pieces drive the most conversions?
How long does the average customer journey take?
User Journey Mapping
Definition and Significance
While marketing funnels provide a high-level view of the conversion process, user journey mapping dives deeper into the customer's actual experience. A user journey map is a visual narrative that chronicles every interaction a customer has with your brand across all touchpoints, capturing not just what they do, but how they think and feel at each stage.
The significance of user journey mapping lies in its ability to:
Reveal gaps between what you think customers experience and what they actually experience
Identify pain points that create friction in the buying process
Uncover opportunities for differentiation and improvement
Foster empathy across your organization by putting everyone in the customer's shoes
Align teams around a customer-centric vision
Key Components of an Effective User Journey Map
A comprehensive user journey map includes several essential elements that bring the customer's experience to life:
1. Persona/User Profile
The journey begins with a clear definition of whose journey you're mapping. This includes:
Demographics and background
Goals and motivations
Challenges and pain points
Technical proficiency
Decision-making authority
2. Stages/Phases
Unlike the marketing funnel's linear stages, journey maps often reveal a more complex, non-linear path:
Research and discovery
Comparison and evaluation
Purchase and onboarding
Use and engagement
Support and renewal
3. Touchpoints and Channels
Every interaction point between the customer and your brand:
Website visits
Social media interactions
Email communications
Customer service calls
Physical store visits
Product usage
4. Customer Actions
What the customer actually does at each stage:
Searches for information
Reads reviews
Compares prices
Requests a demo
Makes a purchase
Contacts support
5. Thoughts and Questions
The internal dialogue running through the customer's mind:
"Can I trust this company?"
"Is this worth the investment?"
"How complicated will implementation be?"
"What if this doesn't work for my specific situation?"
6. Emotions
The emotional journey paralleling the practical one:
Curiosity and excitement
Confusion or frustration
Confidence or anxiety
Satisfaction or disappointment
7. Pain Points and Opportunities
Critical insights that drive improvement:
Where does friction occur?
What causes customers to abandon the journey?
Where can you exceed expectations?
What moments matter most?
Visual Representation of a User Journey Map:

Benefits of Understanding User Pain Points and Motivations
Deep understanding of user pain points and motivations yields transformative benefits:
1. Enhanced Customer Experience
When you know exactly where customers struggle, you can proactively address these friction points. This might mean simplifying a confusing checkout process, providing better documentation, or offering more responsive support at critical moments.
2. More Effective Marketing Messages
Understanding motivations allows you to speak directly to what matters most to your customers. Instead of generic features lists, you can craft narratives that resonate with their specific goals and challenges.
3. Reduced Customer Acquisition Costs
By removing friction from the journey, you increase conversion rates at each stage. This means more customers from the same marketing spend, directly improving your return on investment.
4. Increased Customer Lifetime Value
When you design experiences around actual user needs and motivations, customers are more satisfied, more likely to renew, and more willing to expand their relationship with your brand.
5. Product and Service Innovation
Pain points often reveal unmet needs—opportunities for new products, features, or services that differentiate you from competitors.
Integration of Business Process Automation
How Marketing Funnels and User Journeys Inform Automation Strategies
Marketing funnels and user journey maps aren't just analytical tools—they're blueprints for automation. By understanding the predictable patterns in customer behavior, you can identify opportunities to automate repetitive tasks, deliver timely interventions, and scale personalization.
The Automation Decision Framework:

Funnel-Informed Automation Opportunities:
Awareness Stage:
Automated social media posting schedules
SEO-driven content recommendations
Programmatic advertising bidding and optimization
Chatbots for initial website inquiries
Interest/Consideration Stage:
Behavior-triggered email sequences
Dynamic content personalization based on browsing history
Automated lead scoring and routing
Retargeting campaigns for abandoners
Decision Stage:
Cart abandonment recovery sequences
Automated appointment scheduling
Triggered discount offers based on engagement signals
Automated demo or trial provisioning
Post-Conversion:
Onboarding email sequences
Usage-based engagement campaigns
Renewal reminders and upsell triggers
NPS surveys and feedback collection
Examples of Automated Processes That Enhance Customer Experience
Let's explore concrete examples of how automation, guided by funnel and journey insights, creates superior customer experiences:
Example 1: Intelligent Lead Nurturing
The Journey Insight: Journey mapping reveals that prospects need 3-5 pieces of educational content before they're ready for a sales conversation, and they prefer different content formats based on their role.
The Automation:
Segment leads by role, industry, and behavior
Deploy role-specific content sequences delivered via email
Track engagement and adjust send frequency based on opens and clicks
Automatically notify sales when a prospect reaches a threshold engagement score
Personalize website content based on previous interactions
The Result: Prospects receive relevant information at their own pace, sales teams engage only with qualified leads, and conversion rates increase by 35-50%.
Example 2: Personalized Onboarding Journeys
The Journey Insight: User journey mapping shows that customers with different use cases need different onboarding paths, and those who complete onboarding within the first week have 3x higher retention rates.
The Automation:
Ask new users about their primary use case during signup
Deliver customized tutorial sequences via in-app messages and email
Trigger contextual help based on in-product behavior
Automatically schedule check-in calls for users showing signs of struggle
Celebrate milestone achievements with automated congratulations
The Result: 60% more users complete onboarding, time-to-value decreases by 40%, and long-term retention improves significantly.
Example 3: Proactive Support Automation
The Journey Insight: Journey maps reveal that customers encounter predictable issues at specific points in their journey, and those whose problems are resolved quickly become advocates.
The Automation:
Monitor product usage for error patterns or struggle indicators
Automatically trigger help resources or proactive support outreach
Deploy chatbots for common questions with seamless handoff to humans
Create self-service knowledge bases with AI-powered search
Automatically collect feedback after support interactions
The Result: Support ticket volume decreases by 30%, customer satisfaction scores increase, and support team focuses on complex, high-value issues.
Measuring the Impact of Automation on Conversion Rates
Automation isn't valuable if it doesn't move the needle on business outcomes. Here's how to measure its impact:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Marketing Automation:
Conversion Rate by Stage: Track how automation impacts movement from one funnel stage to the next
Time to Conversion: Measure whether automation accelerates the buying journey
Lead Quality Score: Assess whether automated nurturing improves lead qualification
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculate the efficiency gains from automation
Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) to Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs) Ratio: Evaluate lead nurturing effectiveness
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Determine long-term impact of improved experiences
Measurement Framework:

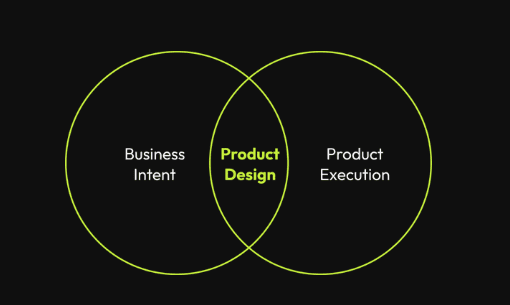
Impact on Product Design
Aligning Product Features with User Needs Identified in Journey Mapping
One of the most powerful applications of user journey mapping is its ability to inform product design decisions. By understanding the jobs customers are trying to accomplish and the struggles they encounter, product teams can prioritize features that deliver genuine value rather than building based on assumptions.
The Journey-to-Product Feedback Loop:

Practical Application:
Imagine your journey mapping reveals that users struggle to compare complex pricing tiers. This pain point might translate into several product design opportunities:
Feature: Interactive pricing calculator that shows cost based on actual usage
Feature: Side-by-side tier comparison with highlighted differences
Feature: "Recommended for you" guidance based on user profile
Feature: Easy upgrade/downgrade functionality with prorated billing clarity
Each feature directly addresses an identified pain point, ensuring your development efforts focus on what customers actually need.
Iterative Design Processes Based on User Feedback
User journey mapping isn't a one-time exercise—it's the foundation for continuous improvement through iterative design. This approach recognizes that:
Initial journey maps are hypotheses to be tested
Customer needs evolve over time
Each product change affects the journey in ways you can't fully predict
The best designs emerge through rapid cycles of building, measuring, and learning
The Iterative Design Cycle:
Map the current journey based on research and data
Identify opportunity areas where experience falls short
Design solutions that address root causes, not just symptoms
Prototype rapidly with low-fidelity mockups or MVPs
Test with real users through usability studies, beta programs, or A/B tests
Gather feedback through both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights
Refine and repeat based on what you learned
This cycle ensures your product evolves in alignment with genuine user needs rather than internal assumptions or competitor mimicry.
Case Studies of Successful Product Design Influenced by User Journeys
Case Study 1: Slack's Onboarding Transformation
The Challenge: Slack's initial onboarding was too open-ended, leaving many new users confused about how to get value from the platform.
Journey Mapping Insights:
Users felt overwhelmed by empty channels
Teams didn't understand the value proposition until they experienced real-time collaboration
Setup friction prevented reaching the "aha moment"
Design Changes:
Implemented guided onboarding with prompts to invite team members immediately
Created templates for common use cases
Added contextual tips that appeared at relevant moments
Streamlined initial channel creation
Results: Activation rates improved significantly, with more users reaching the critical "2,000 messages sent" milestone that correlates with long-term retention.
Case Study 2: Airbnb's Trust and Safety Features
The Challenge: Journey mapping revealed significant anxiety on both sides of the marketplace—guests worried about property accuracy, hosts worried about property damage.
Journey Mapping Insights:
Trust deficit peaked at the booking decision moment
Both parties needed reassurance before commitment
Transparency reduced anxiety more than promotional messaging
Design Changes:
Introduced verified photos program
Implemented comprehensive review system visible before booking
Created host guarantee and guest refund policies
Added real-time messaging prior to booking
Results: Conversion rates improved, customer satisfaction increased, and the platform scaled globally by addressing fundamental trust issues identified through journey mapping.
Case Study 3: Spotify's Personalization Evolution
The Challenge: Users faced decision paralysis with millions of songs available, often defaulting to familiar favorites instead of discovering new music.
Journey Mapping Insights:
Users wanted discovery but feared wasting time on music they wouldn't enjoy
Curation needed to feel personal, not algorithmic
Different contexts demanded different music (workout vs. focus vs. party)
Design Changes:
Developed Discover Weekly, a personalized playlist delivered every Monday
Created mood and activity-based playlists
Implemented collaborative filtering that learned from user behavior
Designed features like Daily Mix that blend familiar and new
Results: Dramatic increases in engagement, listening time, and artist discovery, with Discover Weekly becoming one of Spotify's most valued features.
Conclusion
Marketing funnels and user journey mapping represent far more than analytical exercises or trendy frameworks—they are essential strategic tools for any business seeking sustainable growth and genuine customer satisfaction. By providing clear visibility into how customers discover, evaluate, and experience your products or services, these approaches transform abstract business challenges into concrete opportunities for improvement.
As we've explored throughout this article, the benefits are multifaceted and interconnected:
Marketing funnels give you the structure to understand where prospects are in their buying journey, enabling you to deliver the right message at the right time through the right channel. They reveal bottlenecks and opportunities, turning marketing from an art into a science—one that can be measured, optimized, and continuously improved.
User journey mapping adds the human dimension to this analytical framework, capturing not just what customers do but how they feel, what they think, and where they struggle. This empathy-driven approach ensures that your business decisions are grounded in real customer needs rather than assumptions or wishful thinking.
Business process automation, when informed by these frameworks, becomes genuinely customer-centric rather than merely efficient. You automate the right things—those repetitive interactions that customers want to be seamless—while preserving human touch where it matters most.
Product design becomes targeted and purposeful, with development resources focused on features that address actual pain points and deliver measurable value. This alignment between customer needs and product capabilities is the essence of product-market fit.
Together, these elements create a flywheel effect: better understanding leads to better experiences, which lead to higher conversion and retention, which generate more data and feedback, which deepen your understanding—and the cycle continues, compounding your competitive advantages over time.
Taking Action: Your Next Steps
Understanding these concepts intellectually is just the beginning. The real value comes from implementation. Here's how to get started:
Audit your current state: Do you have documented marketing funnels? Do you know your conversion rates at each stage? Have you mapped user journeys for your key customer segments?
Start with your biggest pain point: Don't try to map everything at once. Focus on the stage with the lowest conversion rate or the journey segment with the most customer complaints.
Involve cross-functional teams: Journey mapping works best when marketing, sales, product, and customer success collaborate. Each team sees different parts of the elephant.
Commit to measurement: Establish baseline metrics before making changes so you can quantify impact.
Embrace iteration: Your first funnel analysis and journey map won't be perfect—and that's okay. The goal is continuous learning and improvement, not perfection.
Invest in the right tools: Whether it's analytics platforms, marketing automation software, or user research tools, equip your team to gather and act on insights efficiently.
The businesses that thrive in today's customer-centric economy are those that truly understand their customers' journeys and systematically remove friction while adding value at every touchpoint. Marketing funnels and user journey mapping provide the framework to make this happen.
As you implement these practices, remember that every business is unique. The specific stages of your funnel, the shape of your customer journeys, and the automation opportunities you discover will be distinct to your context. That's not a limitation—it's your competitive advantage. The companies that win are those that understand their specific customers better than anyone else.
In our next article in this series, we'll dive deep into different types of marketing funnels—from traditional AIDA models to modern subscription funnels, from B2B enterprise sales funnels to e-commerce conversion funnels. We'll explore how to choose the right funnel structure for your business model and optimize each variant for maximum performance.
The journey to customer-centric growth starts with understanding the journey itself. Start mapping today, and watch as clarity transforms into strategy, strategy into action, and action into results.
What aspects of your customer journey are you most curious about? What friction points are your customers experiencing that you'd like to eliminate? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below—your challenges might become the focus of our next deep dive.






